In early March, Afghanistan’s foreign minister, Mawlavi Amir Khan Muttaqi, met with Kazakh Ambassador to Afghanistan Alimkhan Yessengeldiyev and agreed to expand bilateral cooperation in the transport sector. High on the agenda was developing the railway system in Afghanistan. Muttaqi requested technical support from Kazakhstan for new rail line construction.
Kazakhstan has expressed interest in participating in the reconstruction and development of Afghanistan’s infrastructure, especially in the areas of transport, energy, and agriculture. This comes amid efforts to reconnect Afghanistan to world trade and Kazakhstan’s attempts to become a mediator in the region. An informal meeting between Uzbek President Shavkat Mirziyoyev and Kazakh President Kassym-Jomart Tokayev was held prior to the Muttaqi-Yessengeldiyev agreement, and Afghanistan was central to their discussion.
Afghanistan is the third largest buyer of Kazakh grain. The Afghan market traditionally occupies a significant share in the export of grain and flour from Kazakhstan. In 2022 Kazakhstan exported 1.36 million tonnes of wheat flour to Afghanistan, 52 percent more than in 2021, according to APK-Inform, a Central Asian agricultural analytical site.
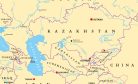
In 2018 a rail route from Kazakhstan to Afghanistan was opened for traffic. The Kostanay-Bolashak-Serhetabad (Turkmenistan) rail route is more than 3,500 kilometers long. It traverses through the Kazakh city of Bolashak and the Turkmen city of Serhetabad, where it crosses the border with Afghanistan to Herat.
In 2022 plans were discussed between Kazakhstan and Turkmenistan for the construction of a grain terminal and elevator at the Turkmen-Afghan border. This grain supply route via Turkmenistan is being promoted by Kazakhstan because it bypasses Uzbekistan, which according to KazAgro, the national grain operator, has traditionally imposed high rates for the transit of grain through Uzbekistan to Afghanistan. However, no Kazakh railroads have been laid yet in Afghanistan. Uzbekistan has been the only country so far that has built and managed a railway line in Afghanistan.
Advancing this cross-border transport development is necessary to prevent a humanitarian crisis and economic collapse in Afghanistan. Indeed the Afghan issue has created a tricky new reality for Kazakhstan and the region as a whole. Central Asian governments see Afghanistan as both a threat and an opportunity.
Underpinning this perception is Afghanistan’s position at the heart of the region. This has resulted in concerted efforts by countries to align their policy in engaging with Afghanistan.
With Russia’s war in Ukraine and Western sanctions on Russia, as well as the U.S. withdrawal from Afghanistan, Central Asia has been forced to make its own contingency plans when it comes to security and trade. In light of this, Kazakhstan and the other Central Asia republics have pursued a strategy with Afghanistan based on the assumption that cooperation and engagement would promote stability. One way they have been going about this is by opening up and testing transport corridors through the country. An example of this is the Uzbek-led Trans-Afghan railway project.
For Kazakhstan, supporting economic development along the north-south axis would see Afghanistan becoming a bridge, not a barrier. In this vision, Kazakhstan hopes to be the convener, facilitator, and engine for change by prying open physical and diplomatic bottlenecks.
The benefits attained through cooperation between Afghanistan and Kazakhstan are obvious for all to see. There is a mutual interest on both sides for cooperation, as the Taliban cannot afford long-term isolation. Economic gains from expanded trade and investment would help diversify Kazakhstan’s transport corridors and bolster Afghanistan’s integration efforts with the wider regional and international community.
That said, Kazakh interests in Afghanistan are challenged by the extreme domestic fragility of the country and the risk of sanctions. Security has remained a key concern in the region, and despite Taliban assurances terrorist activity remains high and widespread.
This has been a key issue for Kazakhstan and has been reflected in Kazakhstan’s efforts to request external support on the Afghan issue. Through the Moscow-led Collective Security Treaty Organization (CSTO), Kazakhstan has been airing its concerns over the unstable situation in Afghanistan and has suggested that the CSTO should increase its focus on securing Central Asia’s southern borders. Other Central Asian countries have expressed the same concern, and the Afghan issue has brought them together. However, fault lines have emerged, with Uzbekistan and Kazakhstan both vying for the mediator role of the region and adopting their own way of working with the Taliban.
With pressure from sanctions, any type of economic interaction with the Taliban government poses a reputational risk to Kazakhstan’s relations with the West. Given the size of Western involvement in Kazakhstan, particularly in its oil and gas sector, this is something that would need to be considered by the Kazakh government.
All that said, transport development is seen as key to both Kazakhstan and Afghanistan’s economic future. Security will continue to be a challenge but without cooperation between Kazakhstan and Afghanistan, the prospects for stability in Central Asia are fairly slim. The spillover effect that could result from an isolated and vulnerable Afghanistan is a risk that Kazakhstan would want to avoid given the January 2022 protests. Kazakhstan must play a key role in restoring trade and communications, and in transforming Afghanistan into a route for licit rather than illicit trade between Central Asia and South Asia.
Much remains to be done, however, and Kazakhstan as well as the other Central Asian states will continue to act in and around Afghanistan, pursuing their national interests as they see them. Looking ahead, Kazakhstan should pursue its desire for cooperation with eyes wide open to make certain that in the process of seeking peace and economic benefit, they do not achieve just the opposite.